Are you a fan of classic DOS games? Have you ever wanted to revisit those nostalgic titles from your childhood, but didn’t know how to get them to run on your modern system? Well, look no further! In this article, we will delve into the world of DOSBox – a powerful program that allows you to play a wide range of DOS games on your computer.
DOSBox is a versatile emulator that can run games from different eras, spanning from the early days of CGA/Tandy/PCjr classics all the way to the gaming milestones of the Quake era. If you’ve always wanted to experience the wonders of games like Commander Keen, Wolfenstein 3D, or Duke Nukem 3D, DOSBox is the way to go.
But don’t worry, we won’t leave you hanging! In the following article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to configure DOSBox to get the most out of your gaming experience. We will walk you through the process of mounting directories, starting games, and troubleshooting common issues like fullscreen display or CD-ROM support. We will also cover topics like mouse control, sound configuration, keyboard input, and game/application speed.
So, if you’re ready to dive into the world of DOS gaming and want to learn more about configuring and optimizing DOSBox, keep reading! We’ve got you covered.
Getting Started with DOSBox
Installing DOSBox
To begin using DOSBox, you will first need to download and install it on your computer. You can find the latest version of DOSBox on the official website, www.dosbox.com. Simply navigate to the downloads page and select the appropriate version for your operating system.
Once the installation file has finished downloading, run it and follow the on-screen instructions to install DOSBox. The installation process is straightforward and should not take long to complete.
Launching DOSBox
After you have successfully installed DOSBox, you can launch it by double-clicking the program icon on your desktop or by navigating to the installation directory and running the DOSBox executable file. Upon launching DOSBox, you will be greeted with the DOSBox command line interface.
Navigating the DOSBox Interface
The DOSBox interface resembles the classic MS-DOS command prompt, with a few additional features and functionalities. From the command line interface, you can execute various commands to navigate through your computer’s file system, mount directories, start games and applications, and customize DOSBox options.
To navigate through directories, you can use common commands such as dir to list the contents of a directory, cd to change to a different directory, and cd .. to move up one directory level.
To execute a command or launch a game/application, simply type the command followed by the Enter key. For example, to start a game that is located in a mounted directory, you would navigate to the directory using the cd command and then type the game’s executable filename to launch it.
Mounting Directories
Understanding File Mounting in DOSBox
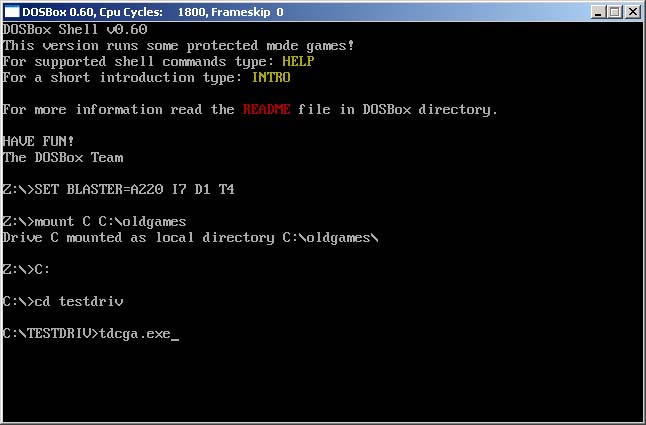
One of the key features of DOSBox is the ability to mount directories from your computer’s file system as virtual drives within the program. This allows you to access and run games and applications that are stored outside of the default DOSBox installation directory.
When you mount a directory, DOSBox assigns it a drive letter, similar to how drives are assigned in MS-DOS. This virtual drive letter can then be used to navigate and execute files within the mounted directory.
Mounting a Directory
To mount a directory in DOSBox, you will need to use the mount command followed by the directory path and the desired drive letter. For example, to mount a directory named “Games” located in the “C:\DOS” folder, you would use the following command:
mount C C:\DOS\Games This command mounts the “Games” directory to the “C” drive within DOSBox. Now, you can navigate to the “C:” drive and access the contents of the mounted directory as if it were a physical drive.
Mounting Multiple Directories
DOSBox allows you to mount multiple directories simultaneously, each with its own virtual drive letter. This can be useful if you have games or applications stored in different directories on your computer.
To mount multiple directories, simply follow the same format as before, but choose a different drive letter for each mounted directory. For example, to mount a second directory named “Utilities” located in the “C:\DOS” folder, you could use the following command:
mount D C:\DOS\Utilities Now, you can access both the “Games” and “Utilities” directories within DOSBox using the “C:” and “D:” drive letters, respectively.
Starting Games and Applications
Using the DOS Command Line
To start a game or application in DOSBox, you will need to use the DOS command line. The command line allows you to execute various commands and launch programs within the DOS environment.
To access the DOS command line in DOSBox, simply launch the program and you will be presented with the command line interface. From here, you can navigate to the directory where the game or application is located and execute it by typing its filename.
For example, if you have mounted a directory called “Games” and you want to start a game named “game.exe”, you would navigate to the “C:” drive (or the appropriate drive letter) and type:
game.exe This will launch the game and you can start playing it within DOSBox.
Launching Games from Mounted Directories
When you have mounted a directory within DOSBox, you can easily start games and applications from that directory using the DOS command line.
To start a game from a mounted directory, you would first navigate to the appropriate drive letter using the cd command. For example, if you have mounted a directory to the “C:” drive, you would type:
C: After navigating to the appropriate drive letter, you can now execute the game’s executable file to start it.
Running Programs from the Internal Drive
In addition to running games and applications from mounted directories, DOSBox also allows you to run programs that are stored within its internal drive.
By default, DOSBox creates an internal drive labeled “Z:” where you can store and run programs directly from within DOSBox. This can be useful if you have games or applications that are specifically designed to run within DOSBox.
To run a program from the internal drive, you would first navigate to the “Z:” drive using the cd command. Afterward, you can execute the program’s executable file to start it.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with its user-friendly interface, you may encounter some common issues while using DOSBox. Here are some troubleshooting tips for resolving common problems you may encounter:
Troubleshooting Fullscreen Display
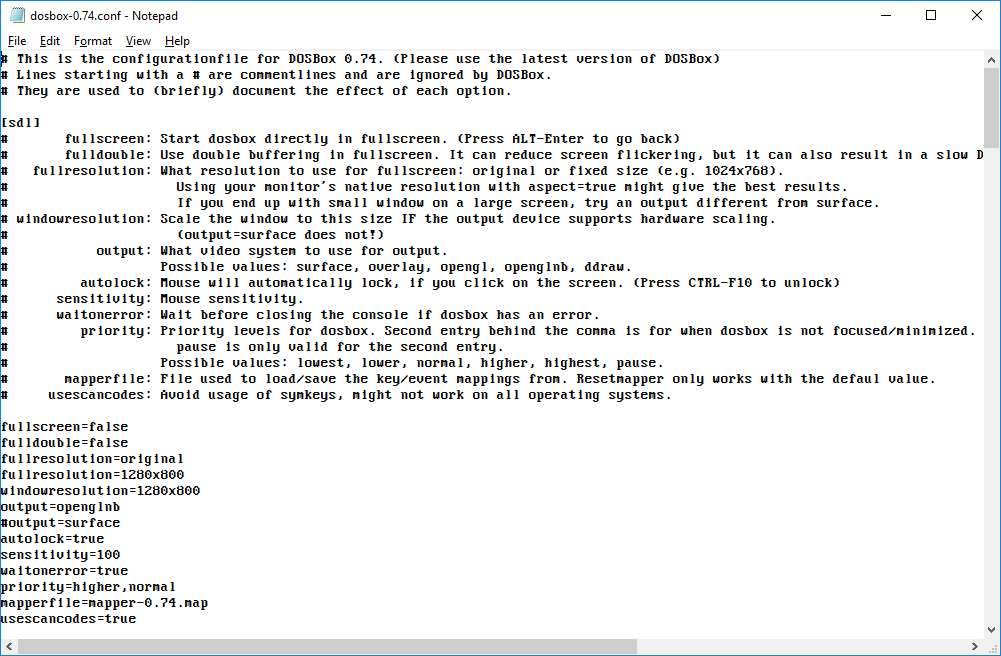
If you experience issues with the fullscreen display while running DOSBox, you can try adjusting the display settings within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file with a text editor and locate the [sdl] section. Here, you can modify options such as fullscreen and fulldouble to optimize the display for your system.
Resolving CD-ROM Support Problems
If you are having trouble accessing CD-ROM support within DOSBox, you may need to configure the CD-ROM settings within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file and locate the [autoexec] section. Here, you can specify the drive letter for your CD-ROM device using the mount command.
Fixing Mouse Control Issues
If you find that mouse control is not working properly within DOSBox, you can try adjusting the mouse options within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file and locate the [sdl] section. Here, you can modify options such as usescancodes and mousemode to improve mouse control compatibility.
Sound Configuration Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues with sound configuration, you can adjust the sound settings within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file and locate the [sblaster] and [speaker] sections. Here, you can configure options such as sbtype, sbbase, irq, and dma to ensure optimal sound performance.
Keyboard Input Troubleshooting
If you experience problems with keyboard input within DOSBox, you can modify the keyboard settings within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file and locate the [dos] section. Here, you can adjust options such as keyboardlayout and keyboardrate to ensure accurate keyboard input.
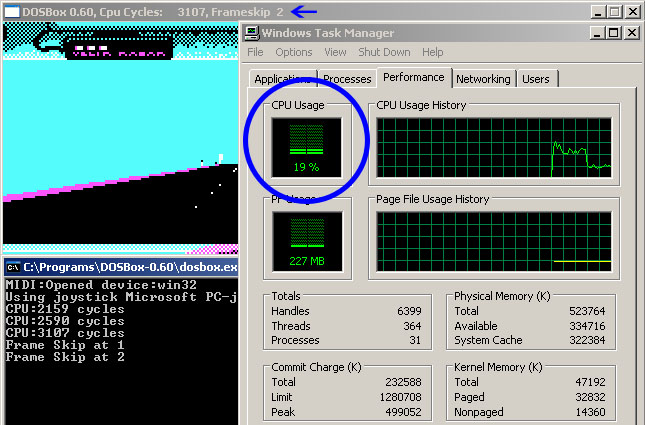
Addressing Game/Application Speed Issues
If you are encountering speed issues while running games or applications within DOSBox, you can adjust the CPU and memory settings within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file and locate the [cpu] and [dos] sections. Here, you can modify options such as cycles and memsize to optimize performance for your system.
Adjusting Sound Settings
Understanding DOSBox Sound Emulation
DOSBox emulates various sound hardware that was common during the MS-DOS era. This allows you to experience the same sound effects and music that were available when these games and applications were originally released.
The sound hardware emulated by DOSBox includes popular sound cards such as AdLib, Sound Blaster, and Gravis Ultrasound. By default, DOSBox is set to emulate the Sound Blaster 16 sound card.
Configuring Sound Hardware
If you want to change the sound card that DOSBox emulates, you can do so by adjusting the sound hardware settings within the DOSBox configuration file. Open the configuration file and locate the [sblaster] section. Here, you can modify options such as sbtype, sbbase, irq, and dma to emulate a different sound card.
For example, if you want to emulate an AdLib sound card, you would set the sbtype option to adlib.
Modifying Sound Settings
In addition to configuring the sound hardware, you can also modify other sound settings within the DOSBox configuration file.
Open the configuration file and locate the [mixer] section. Here, you can adjust options such as rate, blocksize, and prebuffer to fine-tune the sound output.
Experiment with these settings to find the optimal sound configuration for your system and the games or applications you are running.
Customizing DOSBox Options
Locating and Editing the DOSBox Configuration File
To customize the options and settings of DOSBox, you will need to locate and edit the DOSBox configuration file.
The configuration file is a plain text file that contains various sections and options that control the behavior of DOSBox. By modifying these options, you can customize DOSBox to suit your preferences and system specifications.
The configuration file is typically named “dosbox.conf” and can be found in the installation directory of DOSBox. Use a text editor to open the file and make the desired changes.
Changing Display Options
Within the DOSBox configuration file, you can modify display options to optimize the visual output of DOSBox.
Locate the [sdl] section and adjust options such as fullscreen, fulldouble, output, and aspect to suit your display preferences and system capabilities.
Modifying Input Settings
To change the input settings of DOSBox, you will need to locate the [dos] section within the configuration file.
Here, you can modify options such as keyboardlayout, keyboardrate, and joysticktype to customize the input behavior of DOSBox.
Configuring CPU and Memory
To adjust the CPU and memory settings of DOSBox, you will need to locate the [cpu] and [dos] sections within the configuration file.
In the [cpu] section, you can modify options such as core, cycles, and cycleup to optimize CPU performance.
In the [dos] section, you can adjust options such as xms, ems, and umb to allocate memory resources for running games and applications.
Experiment with these options to find the optimal configuration for your system and the games or applications you are running.
Additional Resources
Accessing the DOSBox v0.74-3 Manual
For more detailed information on using DOSBox and its features, you can access the official DOSBox v0.74-3 Manual on the DOSBox website, www.dosbox.com.
The manual provides a comprehensive guide on how to use DOSBox, including detailed instructions on mounting directories, starting games and applications, troubleshooting common problems, adjusting sound settings, customizing options, and more.
Contact Information for DOSBox Support
If you encounter any difficulties or have further questions about using DOSBox, you can find contact information for DOSBox support on the official website, www.dosbox.com.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DOSBox is a powerful program that allows you to run a wide range of DOS games and applications on modern systems. By understanding and utilizing the various configuration and option settings provided by DOSBox, you can enhance your gaming experience and ensure optimal performance.
In this guide, we have covered the basics of installing and launching DOSBox, navigating its interface, mounting directories, starting games and applications, troubleshooting common issues, adjusting sound settings, and customizing options.
Remember to refer to the official DOSBox v0.74-3 Manual for more detailed information and instructions on using DOSBox. With the right configuration and options, you can enjoy the nostalgia of classic DOS games and applications on your modern computer.